Nearly every part of your body is vulnerable to pain. Acute
pain warns us that something may be wrong. Chronic pain can
rob us of our daily life, making it difficult and even unbearable.
What Is Acute Pain?
Acute pain begins suddenly and is usually sharp in quality.
It serves as a warning of disease or a threat to the body. Acute
pain may be caused by many events or circumstances, including:
caused by many events or circumstances, including:
- Surgery
- Broken bones
- Dental work
- Burns or cuts
- Labor and childbirth
Acute pain may be mild and last
just a moment, or it may be severe and last for weeks or months.
In most cases, acute pain does not last longer than six months
and it disappears when the underlying cause of pain has been
treated or has healed. Unrelieved acute pain, however, may lead
to chronic pain.
What Is Chronic Pain?
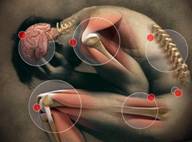 Chronic
pain persists despite the fact that an injury has healed. Pain
signals remain active in the nervous system for weeks, months,
or years. Physical effects include tense muscles, limited mobility,
a lack of energy, and changes in appetite. Emotional effects
include depression, anger, anxiety, and fear of re-injury. Such
a fear may hinder a person's ability to return to normal work
or leisure activities. Common chronic pain complaints include: Chronic
pain persists despite the fact that an injury has healed. Pain
signals remain active in the nervous system for weeks, months,
or years. Physical effects include tense muscles, limited mobility,
a lack of energy, and changes in appetite. Emotional effects
include depression, anger, anxiety, and fear of re-injury. Such
a fear may hinder a person's ability to return to normal work
or leisure activities. Common chronic pain complaints include: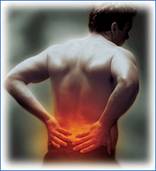
- Headache
- Low Back Pain
- Arthritis pain
- Cancer pain
- Neurogenic pain (pain resulting from damage to nerves)
- Psychogenic pain (pain not due to past disease or
injury or any visible sign of damage inside)
Chronic pain may have originated
with an initial trauma/injury or infection, or there may be
an ongoing cause of pain. However, some people suffer chronic
pain in the absence of any past injury or evidence of body damage.
Measuring Pain
The World Health Organization
has a "pain ladder" with 3 steps. The steps are mild
pain, moderate pain, and severe pain.
- Mild pain: Mild pain is self-limited. It goes away either
with no therapy at all or with the use of nonprescription
medication such as acetaminophen (Tylenol), aspirin, or other
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Moderate pain: Moderate pain is worse than mild pain. It
interferes with function. You may be unable to ignore the
pain and go on with all of the activities of daily living,
but it goes away after a while and doesn't come back after
it has been treated.
- Severe pain: Severe pain is defined as pain that interferes
with some or all of the activities of daily living. You may
be confined to bed or chair rest because of the severity of
the pain. Often, it doesn't go away, and treatment needs to
be continuous for days, weeks, months, or years.
According to the American Pain
Foundation, there are more than 50 million Americans suffering
from chronic pain, or 25 million experiencing acute pain as
a result of injury or surgery.
How Is Pain Treated?
Depending upon its severity, pain may be treated in a number
of ways. Symptomatic options for the treatment of pain may include
one or more of the following:
- Drug treatments such as non-prescription medications like
Aleve, Motrin and Tylenol or
 stronger
medications such as morphine, codeine or anesthesia. stronger
medications such as morphine, codeine or anesthesia.
- Nerve blocks (the blocking of a group of nerves with local
anesthetics)
- Alternative treatments such as acupuncture, relaxation
and biofeedback.
- Electrical stimulation
- Physical therapy
- Surgery
- Psychological counseling
- Behavior modification
If you're a pain sufferer, here's
some good news: Plenty of options exist to ease aches, and many
of them don't come in pill form. After all, modern drugs only
entered the market recently, and arthritis, menstrual cramps,
post-surgery pain, and other aches and pains soothed by the
drug have been around and managed for a much longer time period.
The Treatment of Pain with Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Easing pain with needles may
sound agonizing, but acupuncture is an ancient form of pain
relief.
 In the treatment of pain, the primary difference between
Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine is that TCM
methods such as acupuncture and herbal treatments have virtually
no side effects. This is because acupuncture works in an entirely
different manner. For example, the NSAIDs commonly used to relieve
pain provide short-term relief by blocking the production of
pain-creating substances called prostaglandins. But in addition
to creating pain, prostaglandins are also vasodilators, which
help enhance circulation. Therefore inhibiting their production
has the harmful side effect of decreasing blood supply to the
muscles and joints, which ultimately slows the recovery process.
In the treatment of pain, the primary difference between
Traditional Chinese Medicine and Western Medicine is that TCM
methods such as acupuncture and herbal treatments have virtually
no side effects. This is because acupuncture works in an entirely
different manner. For example, the NSAIDs commonly used to relieve
pain provide short-term relief by blocking the production of
pain-creating substances called prostaglandins. But in addition
to creating pain, prostaglandins are also vasodilators, which
help enhance circulation. Therefore inhibiting their production
has the harmful side effect of decreasing blood supply to the
muscles and joints, which ultimately slows the recovery process.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM)
creates an entirely opposite effect. Acupuncture, tui na and
herbal applications work to stimulate the central nervous system,
which in turn releases chemicals into the muscles, spinal cord
and brain. These chemicals either alter the perception of pain
or release other chemicals that influence the body's self-regulating
systems. These biochemical changes support the body's natural
healing abilities, improve circulation, and promote physical
and emotional well-being. When circulation in the tissue improves,
muscle relaxation occurs and pain is reduced. In some cases,
improved circulation may cause the pain to increase, but this
is followed by accelerated repair of the tissue. Proper circulation
is important not only for the blood to nourish the tissue, but
also for eliminating muscle fatigue and pain-causing substances
such as lactic acid.
In 1997, the National Institutes of Health
(U.S.) officially recognized acupuncture as an effective treatment
for pain.  According
to the 1997 NIH panel, clinical studies showed that acupuncture
therapy is helpful in treating many types of chronic pain, including
headaches, menstrual cramps, tennis elbow, fibromyalgia, myofascial
pain, osteoarthritis, neck pain, low back pain and carpal tunnel
syndrome. Recent studies also suggest that topical herbal compounds
like those used in Traditional Chinese Medicine are very effective
for reducing chronic pain. According
to the 1997 NIH panel, clinical studies showed that acupuncture
therapy is helpful in treating many types of chronic pain, including
headaches, menstrual cramps, tennis elbow, fibromyalgia, myofascial
pain, osteoarthritis, neck pain, low back pain and carpal tunnel
syndrome. Recent studies also suggest that topical herbal compounds
like those used in Traditional Chinese Medicine are very effective
for reducing chronic pain.
|